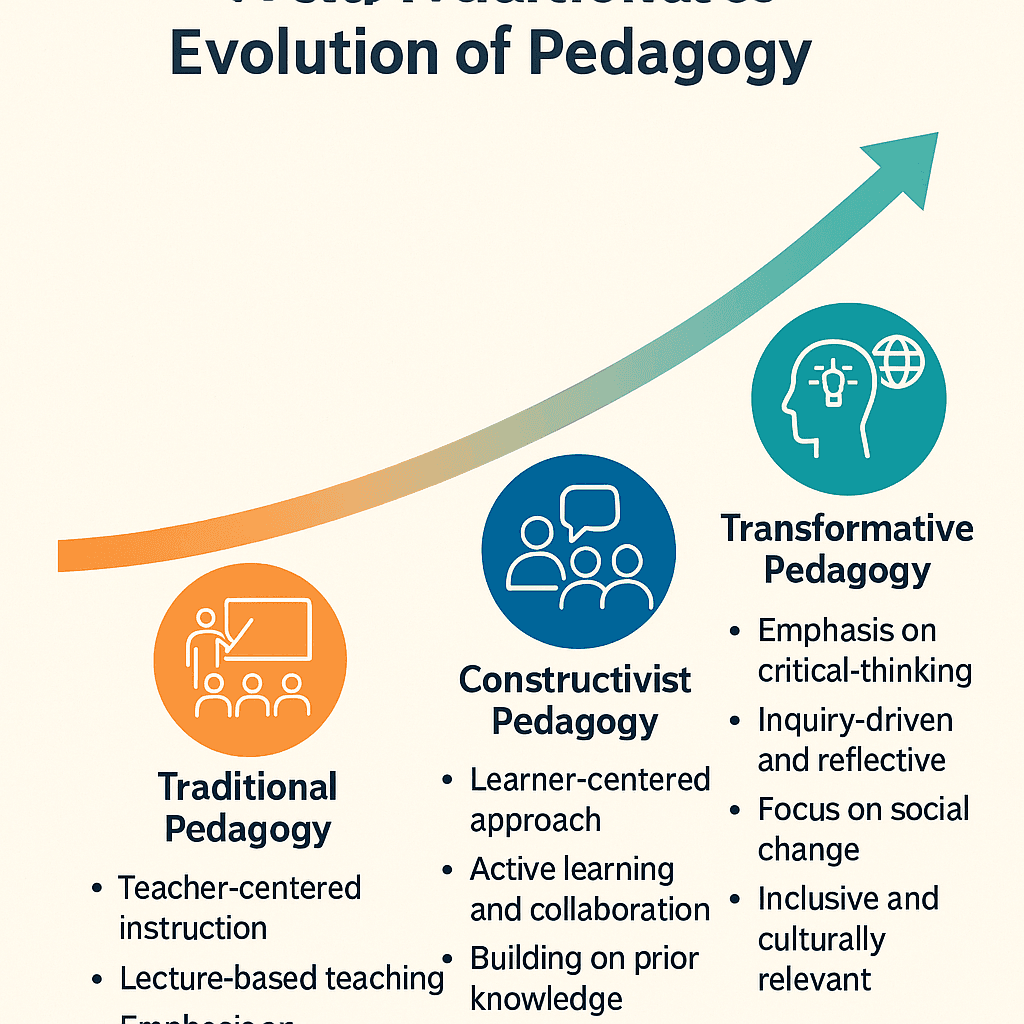
Pedagogy—the art and science of teaching—has undergone profound change over the past century. The shift from teacher-centred instruction to learner-centred approaches marks a critical chapter in the evolution of pedagogy. Today, teaching is no longer just about transferring knowledge; it is about cultivating critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration in dynamic and inclusive learning environments.
This post explores how pedagogy has evolved, compares traditional and modern methods, and highlights the transformative practices redefining 21st-century education.
The Role of Case Studies in Academic Research: Best Practices
1. Traditional Pedagogy: A Foundation Rooted in Authority and Rote Learning
In traditional classrooms, the teacher is the central figure of authority, and learning is a linear, structured process. The focus is on content mastery, memorisation, and standardised assessment.
Characteristics of traditional pedagogy:
- Teacher-centred instruction
- Passive student roles
- Emphasis on lectures and textbooks
- Rigid curriculum and fixed outcomes
- Uniform teaching styles across learners
Example:
A history teacher delivers a lecture while students take notes. Learning is assessed through a multiple-choice test at the end of the unit.
While this model has ensured discipline and content consistency, it often limits creativity, critical inquiry, and personalised learning.
2. The Shift Toward Constructivist and Progressive Models
From the early 20th century, educational theorists like John Dewey and Jean Piaget began challenging traditional pedagogy. Their work laid the foundation for constructivist approaches, where learning is viewed as an active, social, and student-driven process.
Key changes introduced:
- Active learning through discussion, problem-solving, and projects
- Emphasis on student experiences and prior knowledge
- Learning as a process of discovery and reflection
- Focus on skills, not just facts
Example:
In a modern science classroom, students work in groups to design a simple experiment, collect data, and present their findings. The teacher acts as a facilitator rather than a lecturer.
3. Transformative Pedagogy: Teaching for Empowerment and Social Change
In recent decades, transformative pedagogy has emerged as a response to the need for inclusive, socially responsive, and future-focused education. This approach aims not just to educate but to empower learners to become change-makers in their communities and professions.
Core elements of transformative pedagogy:
- Learner-centred and inquiry-driven
- Emphasis on critical thinking and real-world application
- Integration of technology and digital fluency
- Culturally responsive and inclusive practice
- Collaboration, reflection, and social responsibility
Example:
A civic studies teacher guides students to identify a local environmental issue, research it, and propose a solution to present to their local council. Learning is embedded in real-world relevance and critical citizenship.
4. Technology-Enhanced Learning: A Catalyst for Pedagogical Change
The integration of digital tools has accelerated the evolution of pedagogy. Online platforms, AI-powered feedback systems, virtual labs, and collaborative apps have transformed how, when, and where learning occurs.
Impact of educational technology:
- Enables blended and flipped classroom models
- Supports personalised learning pathways
- Enhances accessibility for learners with disabilities
- Fosters global collaboration and knowledge exchange
- Offers real-time analytics to improve teaching strategies
Example:
A university course on global health includes live webinars, AI-generated feedback on student essays, and discussion forums connecting learners across continents.
5. Culturally Responsive and Inclusive Pedagogy
Transformative education is not just about methodology—it is about equity and inclusion. Educators are now adopting approaches that acknowledge and celebrate students' diverse identities, languages, and worldviews.
Principles of inclusive pedagogy:
- Valuing cultural diversity in curriculum design
- Adapting teaching to different learning needs
- Building safe, respectful, and affirming environments
- Encouraging student voice and participation
Example:
An English teacher includes literature from a range of cultures and invites students to share stories from their own backgrounds, validating multiple perspectives.
6. Pedagogy of the Future: Trends to Watch
Looking ahead, the evolution of pedagogy will likely continue along paths that prioritise:
- Artificial intelligence and adaptive learning
- Competency-based and micro-credential learning
- Interdisciplinary and experiential education
- Sustainability and global citizenship
- Ethical AI and digital literacy in all subject areas
Educational systems that embrace these trends are better positioned to prepare learners for complex, fast-changing futures.
Conclusion
The journey from traditional to transformative in the evolution of pedagogy reflects a deeper shift in how we understand learning and the role of educators. Today’s best teaching practices are learner-focused, inclusive, tech-enabled, and socially responsive.
Educators who continuously adapt their pedagogy to meet the needs of modern learners are not only more effective but also more impactful. Whether you're designing curriculum, leading professional development, or teaching in a classroom, recognising the past and embracing the future of pedagogy is essential to meaningful education reform.
Visit The Case HQ for 95+ courses
Read More:
Critical Analysis: How Students Use Gen AI for Essay Writing—Should We Be Concerned?
Essential Comparison of CLSSGB vs CSSGB: Which Six Sigma Green Belt Is Right for You?
Powerful Guide to Writing Exam Questions Using Gen AI Effectively
Time-Saving Power of Using ChatGPT to Generate Lesson Plans in Minutes
Essential Guide: What Is Generative AI and Why Should Educators Care?
Innovative Ways Art & Design Schools Use AI for Portfolio Assessments
Certified AI Business Strategist (CAIBS): Career ROI That Pays Off Fast
Is CAIBS Right for You? Eligibility & Readiness for the Certified AI Business Strategist Program
https://thecasehq.com/from-traditional-to-transformative-the-evolution-of-pedagogy-in-modern-education/?fsp_sid=1227
Comments
Post a Comment