Choosing the right research method is one of the most critical decisions in the academic or professional research process. The debate of quantitative vs qualitative is central to this decision, as each method offers distinct advantages depending on your research aims, questions, and context.
In this article, we demystify the quantitative vs qualitative debate, provide practical examples, and help you determine which method or combination is most suitable for your study.
Designing Transparent Rubrics for AI-Based Evaluation: A Practical Guide for Educators
What Is Quantitative Research
Quantitative research involves collecting and analysing numerical data to identify patterns, relationships, or trends. It is objective, structured, and typically focuses on measurable variables.
Key characteristics include:
- Based on statistical analysis
- Uses tools such as surveys, experiments, or secondary datasets
- Aims to test hypotheses or measure variables
- Results are often generalisable to larger populations
Example:
A researcher studies the impact of remote learning on high school performance by surveying 500 students. The data is analysed using statistical software to determine if there is a significant correlation between screen time and exam results.
What Is Qualitative Research
Qualitative research explores human experiences, behaviours, and perceptions. It is interpretive, open-ended, and aims to understand the why and how behind phenomena.
Key characteristics include:
- Focuses on meaning and context
- Uses interviews, focus groups, and observations
- Produces textual, visual, or audio-based data
- Aims for depth and insight rather than generalisation
Example:
A researcher conducts in-depth interviews with 15 teachers to explore their experiences of remote teaching during the pandemic. Thematic analysis is used to identify common challenges and strategies.
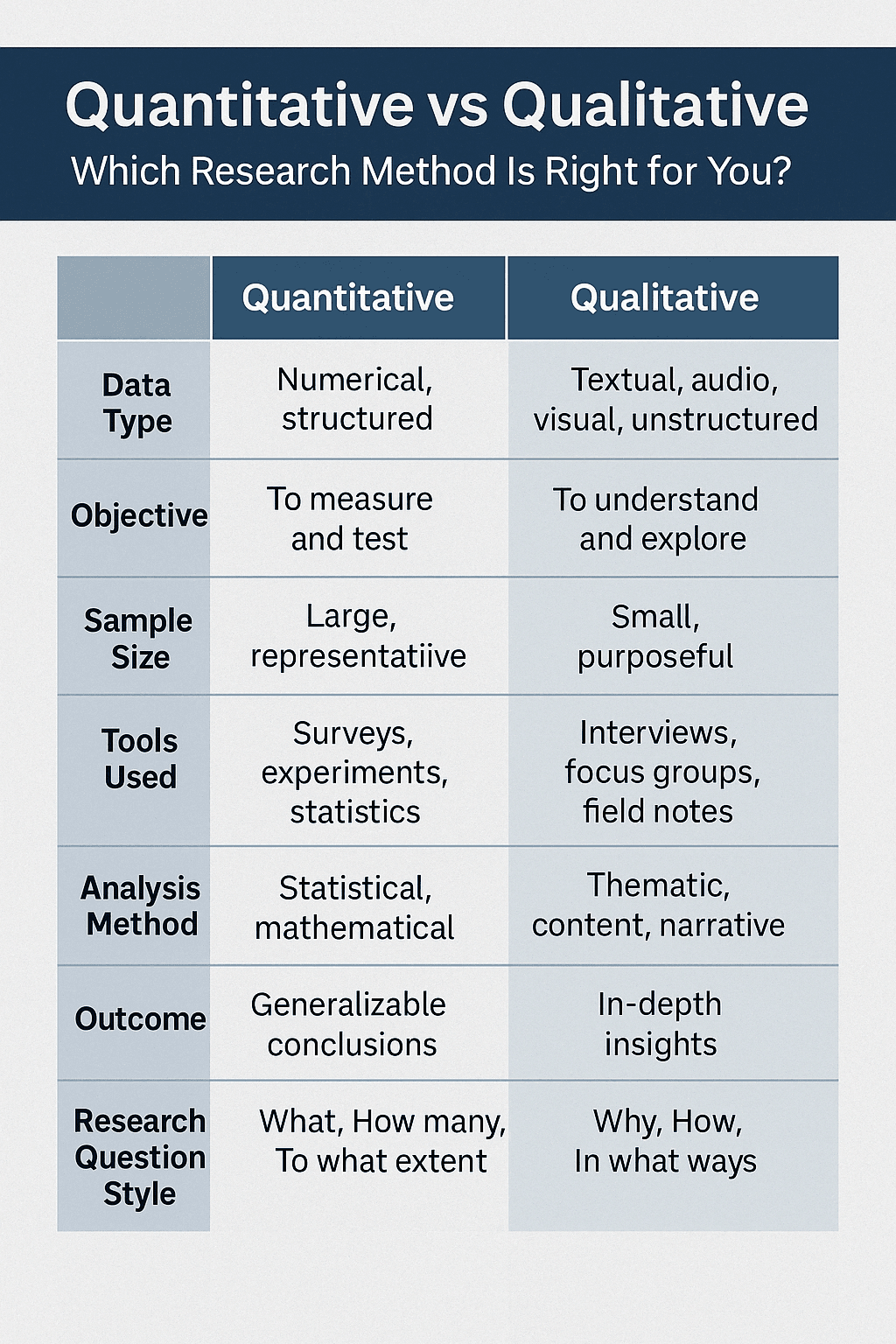
Quantitative vs Qualitative: Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantitative | Qualitative |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Numerical and structured | Textual, audio or visual, unstructured |
| Objective | To measure and test | To explore and understand |
| Sample Size | Large and representative | Small and purposeful |
| Tools Used | Surveys, experiments, statistics | Interviews, focus groups, field notes |
| Analysis Method | Statistical and mathematical | Thematic, content or narrative analysis |
| Outcome | Generalisable conclusions | In-depth contextual insights |
| Research Question Style | What, How many, To what extent | Why, How, In what ways |
How to Choose Between Quantitative and Qualitative Research
Choosing between quantitative vs qualitative research depends on several factors:
- Nature of the Research Question
Use quantitative methods if your goal is to measure relationships, test hypotheses, or identify patterns.
Use qualitative methods if you aim to explore perceptions, motivations, or social processes.
Example:
Quantitative: What percentage of university students experience exam-related anxiety
Qualitative: How do university students describe their experience of exam-related anxiety
- Desired Outcome
Quantitative methods are ideal for producing statistically significant results.
Qualitative methods are more suitable for rich, in-depth understanding. - Type of Data You Can Access
If large-scale numeric data is available, quantitative research may be appropriate.
If access is limited to participants or experiences, qualitative research could be more effective. - Time and Resources
Quantitative research often requires access to large samples and statistical tools but is generally faster to analyse.
Qualitative research involves time-intensive data collection and interpretation but yields nuanced insights.
Combining Both Methods: The Mixed-Methods Approach
Sometimes, a combination of both approaches offers the best solution. A mixed-methods design integrates both quantitative and qualitative data collection and analysis, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding.
Example:
A study on workplace wellbeing could begin with a quantitative survey to assess job satisfaction (n=300), followed by qualitative interviews (n=20) to explore employee experiences in greater depth.
Benefits of mixed-methods research include:
- Broader understanding of the topic
- Validation of results through triangulation
- Ability to explore both patterns and meanings
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Selecting a method purely based on convenience rather than appropriateness
- Using quantitative tools for questions better suited to qualitative inquiry
- Ignoring patterns or structure in qualitative data
- Overlooking the importance of aligning the method with the research question and objectives
Conclusion
In the quantitative vs qualitative debate, neither method is superior. The right choice depends on the purpose of your research, the nature of your questions, and the resources available to you. Each method has strengths and limitations, and both contribute uniquely to the research process.
By carefully considering your objectives and understanding the characteristics of each approach, you can select the most appropriate method or combination to produce credible, relevant, and impactful research.
Visit The Case HQ for 95+ courses
Read More:
Critical Analysis: How Students Use Gen AI for Essay Writing—Should We Be Concerned?
Essential Comparison of CLSSGB vs CSSGB: Which Six Sigma Green Belt Is Right for You?
Powerful Guide to Writing Exam Questions Using Gen AI Effectively
Time-Saving Power of Using ChatGPT to Generate Lesson Plans in Minutes
Essential Guide: What Is Generative AI and Why Should Educators Care?
Innovative Ways Art & Design Schools Use AI for Portfolio Assessments
Transformative Power of AI for Assessment Dashboards and Performance Reports
Top-Rated AI Assessment Tools for Schools and Universities in 2025
Gamification in Education: Beyond Points and Badges – Strategies That Truly Engage
High-Impact Blended Learning Models That Work in 2025
Step-by-Step Guide: Backward Design in Course Planning for Effective Teaching
From Traditional to Transformative: The Evolution of Pedagogy in Modern Education
Emerging Trends: The Role of AI in Doctoral Supervision
Top Picks: Best AI Tools for Academic Researchers in 2025
https://thecasehq.com/quantitative-vs-qualitative-which-research-method-is-right-for-you/?fsp_sid=2130
Comments
Post a Comment