Artificial Intelligence is transforming the workplace at record speed. While companies still hire AI specialists like data scientists, prompt engineers, or AI ethicists a new type of professional is on the rise in 2025: the AI Generalist.
Unlike narrow specialists, an AI Generalist is someone who understands how to use AI across multiple business functions, applying it flexibly to solve diverse problems. But the question remains: Should you aim to become one?
This article explores the rise of the AI Generalist, what the role entails, the skills required, and whether it’s the right career move for you.
What Is an AI Generalist?
It is not tied to one technical specialty. Instead, they:
- Use AI tools in multiple domains (marketing, HR, operations, strategy).
- Understand enough technical basics to collaborate with engineers.
- Apply AI ethically, strategically, and creatively across business contexts.
Think of a “translator” between technical AI teams and business functions.
Why Rising in Demand
- Cross-functional AI adoption – Every department (finance, HR, supply chain) now uses AI, but most lack in-house expertise.
- Bridging skill gaps – Specialists often struggle to explain AI to non-technical stakeholders. AI Generalists fill that gap.
- Agility in disruption – Companies value employees who can quickly adapt AI to changing needs.
According to Gartner (2025), demand for AI Generalist roles has grown by 42% year-over-year.
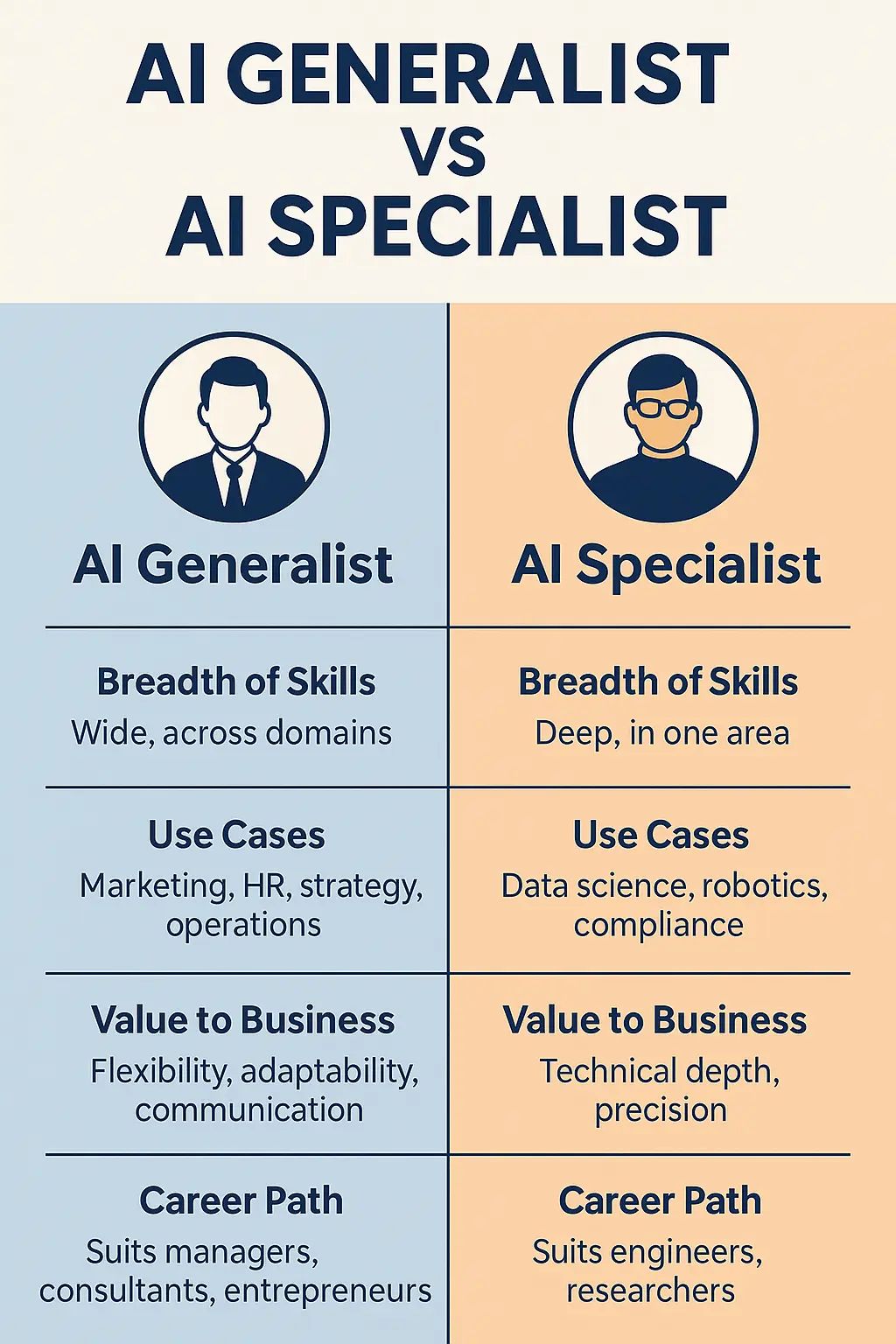
AI Generalist vs AI Specialist
| Aspect | AI Generalist | AI Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Breadth of skills | Wide, across domains | Deep, in one area |
| Use cases | Marketing, HR, strategy, operations | Data science, robotics, compliance |
| Value to business | Flexibility, adaptability, communication | Technical depth, precision |
| Career path | Suits managers, consultants, entrepreneurs | Suits engineers, researchers |
The best organizations need both, particularly valuable for leadership and innovation roles.
Skills You Need
- AI Literacy – Understanding AI models, generative AI, and automation basics.
- Prompt Engineering – Knowing how to interact with AI effectively.
- Business Application – Translating AI into marketing, HR, finance, and operations.
- Ethics & Governance – Awareness of compliance frameworks like ISO/IEC 42001.
- Communication & Storytelling – Explaining AI insights to non-technical audiences.
Real-World Example: AI Generalist in Action
Case 1: A mid-level manager at a retail company learned to use AI for inventory forecasting, marketing copy, and customer service chatbots. Instead of hiring three specialists, the company promoted him into an AI Generalist role, leading cross-departmental AI adoption.
Case 2: A startup founder with no coding background leveraged AI tools for product design, HR hiring, and finance forecasting. This AI Generalist skillset helped the company grow without a large specialist team.
Pros
- Versatility – Work across different industries and functions.
- Leadership pathway – Generalists often move into management faster.
- Future-proofing – As AI changes rapidly, broad adaptability is an advantage.
Cons
- Shallower expertise – May struggle in highly technical conversations.
- Competition with specialists – Some roles (e.g., AI research) will always require deep expertise.
- Risk of “jack of all trades” – Employers may undervalue if not tied to measurable business impact.
Should You Become an AI Generalist?
You should consider pursuing an AI Generalist career if you are:
- Already working in business, HR, education, healthcare, or consulting.
- Strong at communication, problem-solving, and cross-functional collaboration.
- Interested in leadership roles that require broad oversight.
If you’re more passionate about algorithms, robotics, or research, a specialist track may be better.
Conclusion: The Future Belongs to AI Generalists and Specialists
The rise of the AI Generalist reflects a new reality: businesses don’t just need experts in code they need professionals who can connect AI with strategy, operations, and people.
For many professionals without a technical degree, becoming an AI Generalist is the most practical path into the booming AI economy. It’s not about being a master coder, but about mastering how to apply AI across diverse contexts.
Want to future-proof your career? Explore cross-functional AI certifications at TheCaseHQ to begin your journey as an AI Generalist.
Visit our other human resource certifications
Visit our other artificial intelligence certifications
Visit our other digital technology certifications
Visit our other higher education certifications
Visit our other quality and lean six sigma certifications
Visit our other strategy and management certifications
The Rise of Intelligent Tutoring Systems: A New Era in Education
AI and the Future of Assessment: From Standardized Tests to Adaptive Learning
AI in Early Childhood Education: Promises and Pitfalls
How AI is Shaping the Role of Educators in the 21st Century
AI and Special Education: Customizing Learning for Every Student
https://thecasehq.com/ai-generalist-the-rise-of-the-ai-generalist/?fsp_sid=4540
Comments
Post a Comment