Universities are rapidly adopting artificial intelligence to transform how students are evaluated. From grading essays to detecting plagiarism and tracking participation, AI-Powered Assessment is becoming the silent engine of higher education in 2025. But while institutions highlight efficiency and fairness, there’s much more happening behind the scenes.
This article uncovers the reality of AI-Powered Assessment, the opportunities, risks, and what universities often don’t tell students and faculty.
What Is AI-Powered Assessment?
AI-Powered Assessment refers to the use of artificial intelligence to evaluate learning outcomes, performance, and skills. Instead of relying solely on human graders, universities now deploy AI systems to:
- Score written essays and reports
- Analyze participation in online classes
- Detect plagiarism and contract cheating
- Provide personalized feedback in real time
While marketed as objective and efficient, AI-Powered Assessment raises critical questions about fairness, bias, and transparency.
Why Universities Push AI-Powered Assessment
- Efficiency – Reduces grading workload for faculty.
- Scalability – Handles thousands of assignments quickly in large classes.
- Cost Reduction – Cuts reliance on human graders and external examiners.
- Data Insights – Provides analytics on student performance trends.
Universities highlight these benefits but rarely share the hidden trade-offs.
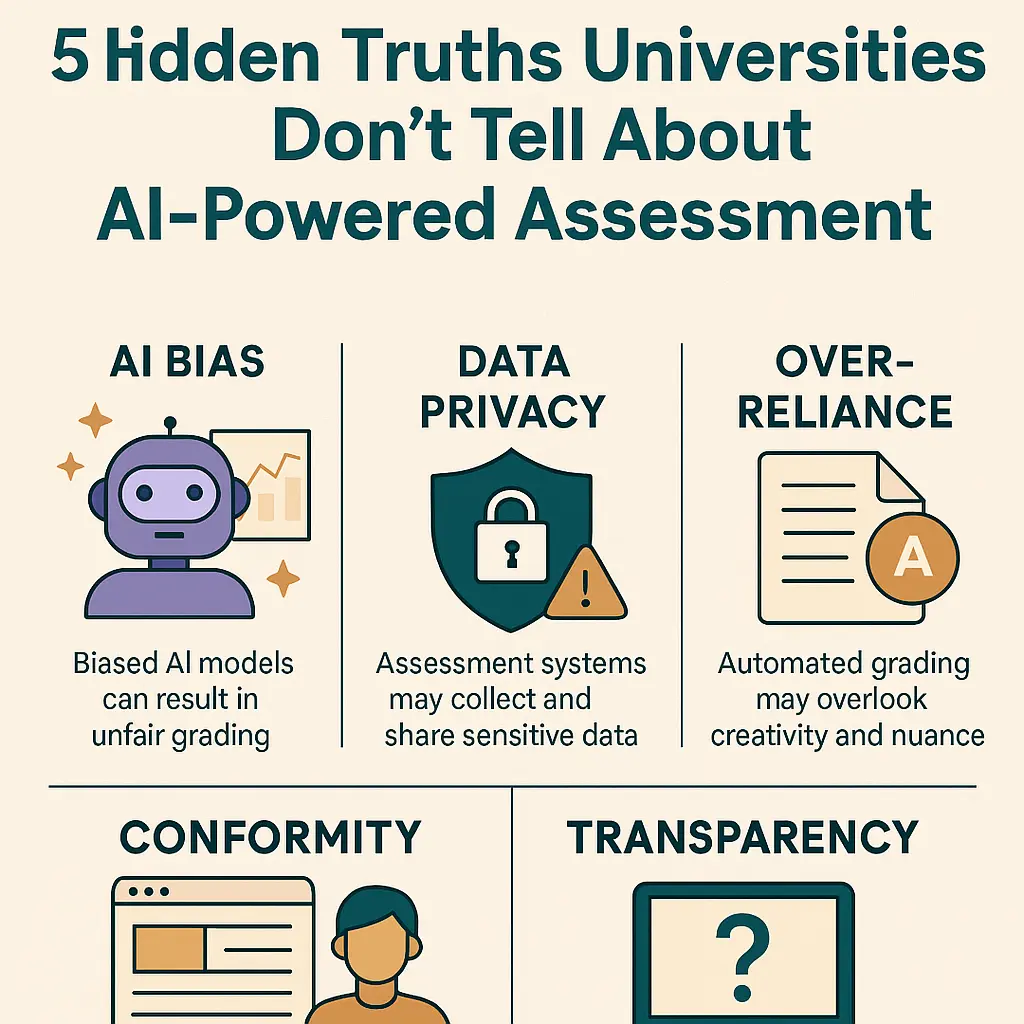
What Universities Don’t Tell You About AI-Powered Assessment
1. AI Bias Can Impact Your Grades
AI models are trained on historical data, which may reflect bias in grading patterns. Students from non-traditional backgrounds may find their work unfairly marked down.
- Example: A student writing in a second language may be penalized for grammar, even if ideas are strong.
- Hidden truth: Few universities publicly disclose how their AI grading models are trained.
2. Data Privacy Is at Risk
To function, AI-Powered Assessment systems collect massive amounts of data essays, participation logs, even keystroke patterns.
- Risk: Universities may share data with third-party vendors.
- Hidden truth: Many institutions lack clear consent policies for how long student data is stored or who has access.
3. Over-Reliance on Automated Grading
AI feedback may encourage surface-level improvements (grammar, structure) but fail to recognize creativity, nuance, or cultural context.
- Example: A student writing a unique, unconventional essay could score lower than a formulaic one.
- Hidden truth: Many professors quietly adjust AI-generated grades but this isn’t disclosed.
4. Pressure to Conform
AI systems often favor standardized writing styles. Students may feel pressured to write “for the algorithm” rather than for intellectual exploration.
- Result: Education risks shifting from critical thinking to pattern replication.
5. Limited Transparency
Universities rarely provide details about the algorithms behind AI-Powered Assessment. Students may not know:
- How final grades are calculated
- How much weight AI has vs human markers
- Whether appeals against AI grades are possible
Opportunities in AI-Powered Assessment
Despite risks, AI-Powered Assessment also opens doors:
- Personalized Feedback – Instant suggestions help students improve faster.
- Learning Analytics – Identifies struggling students early.
- Accessibility – Assists students with disabilities through adaptive assessments.
- Global Scalability – Enables fairer evaluation in MOOCs and online courses.
Case Study 1: Automated Essay Scoring
At a U.S. university, AI tools now score thousands of freshman essays. Faculty save time, but students report frustration when “rigid algorithms” penalize creative writing styles.
Case Study 2: Plagiarism & Contract Cheating Detection
Universities increasingly use AI to flag suspicious writing patterns. While effective, false positives sometimes wrongly accuse students, leading to stressful appeals.
Case Study 3: Adaptive Learning in STEM
AI-driven quizzes in engineering programs adjust difficulty based on student performance. This enhances learning but raises questions about whether adaptive paths disadvantage slower learners.
The Ethics Debate Around AI-Powered Assessment
- Transparency: Should students know when and how AI contributes to grades?
- Accountability: Who is responsible for grading errors — the AI or the institution?
- Equity: How do we prevent reinforcing bias against underrepresented groups?
- Human Oversight: Should every AI grade require human review?
These are the issues universities prefer to gloss over when marketing AI adoption.
What Students and Faculty Should Do
- Ask Questions – Request transparency about how AI-Powered Assessment systems are trained and used.
- Demand Oversight – Advocate for human-in-the-loop grading, especially for high-stakes exams.
- Protect Your Data – Understand privacy policies before submitting assessments.
- Use AI Responsibly – Leverage AI feedback as a supplement, not a substitute, for critical thinking.
The Future of AI-Powered Assessment
By 2030, most universities will integrate AI-Powered Assessment as standard practice. But the winners will be institutions that:
- Balance efficiency with fairness
- Maintain transparency with students
- Keep human judgment central to education
Conclusion: What Universities Don’t Want to Admit
AI-Powered Assessment is here to stay, but the truth is more complex than the glossy brochures suggest. Behind claims of efficiency and fairness lie real risks of bias, privacy invasion, and conformity pressures.
For students, the best strategy is awareness and advocacy. For faculty, it’s maintaining a balance between AI efficiency and human academic judgment.
Ultimately, the goal should not be replacing educators but enhancing education with AI. Only then can AI-Powered Assessment deliver on its promise without compromising trust and fairness.
Visit our other human resource certifications
Visit our other artificial intelligence certifications
Visit our other digital technology certifications
Visit our other higher education certifications
Visit our other quality and lean six sigma certifications
Visit our other strategy and management certifications
Read more:
Critical Role of AI Tools in Preserving Academic Integrity in Education
Powerful Tools and Techniques for AI in Formative Assessment
Transforming Summative Assessments with AI: A Smarter Future for Education
How AI in Grading Rubrics Ensures Unmatched Consistency and Fairness in Education
Powerful Adaptive Learning Paths: How AI Tailors Assessments to Learners’ Needs
Revolutionary AI-Powered Assessment Tools Are Transforming Education Forever
Practical Applications of Generative AI in Education: Turning Innovation into Daily Practice
https://thecasehq.com/ai-powered-assessment-2025/?fsp_sid=4732
Comments
Post a Comment